How are humanoid robots changing the military and defense? These advanced machines are revolutionizing modern warfare by performing high-risk tasks and reducing human casualties. In this article, we explore the roles, advantages, types, and ethical considerations of humanoid robots in military and defense, offering insights into their expanding impact.
Key Takeaways
- Humanoid robots in military operations provide cost-effectiveness, precision, and the potential to lower human casualties by taking over dangerous tasks and roles previously performed by human soldiers.
- Various types of humanoid robots, including ground robots, airborne humanoids, and autonomous systems, serve distinct functions such as transportation, surveillance, combat, and search-and-rescue missions, enhancing military capabilities and operational efficiency.
- The deployment of military robots raises significant ethical and legal concerns, including increased likelihood of warfare, civilian casualties, and accountability for autonomous actions, prompting efforts to establish rules and ethical guidelines for their use.
The Role of Humanoid Robots in Modern Warfare
Military robots, whether autonomous or remote-controlled, have become integral to modern warfare. Their journey began in the mid-20th century with devices like the German Goliath tracked mines and Soviet teletanks, which were used during World War II and the Cold War. These early iterations were far from the sophisticated machines we see today, but they laid the groundwork for future advancements.
The U.S. Army uses army robots that resemble human soldiers in current military drills, complete with camera lenses and sheet metal skin. These robots serve as valuable tools for preparing the human soldier for real-world combat scenarios, providing a safe and controlled environment for training.
Ongoing research suggests that the reliance on autonomous weapons in modern warfare will grow. These future robots will likely be more autonomous, capable of performing complex tasks with minimal human intervention, thus reshaping the dynamics of armed conflict.
Key Advantages of Humanoid Robots in Defense
Several significant advantages come with the incorporation of humanoid robots into defense operations. One of the most compelling benefits is cost-effectiveness. Unlike human soldiers, humanoid robots require less maintenance and have lower ongoing costs. This economic efficiency allows military forces to allocate resources to other critical areas without compromising operational capabilities.
Precision is another crucial advantage. Humanoid robots are programmed to perform tasks with minimal errors, thereby reducing collateral damage during operations. Their ability to make split-second decisions based on pre-set rules ensures adherence to military doctrine without the emotional interference that can affect human judgment.
The potential to lower human casualties might be the most significant benefit. By removing soldiers from direct combat scenarios, humanoid robots can take on dangerous tasks, ensuring that fewer human lives are at risk. This not only preserves human life but also allows for more strategic deployment of human personnel in less hazardous roles.
Types of Humanoid Robots Used by Military Forces
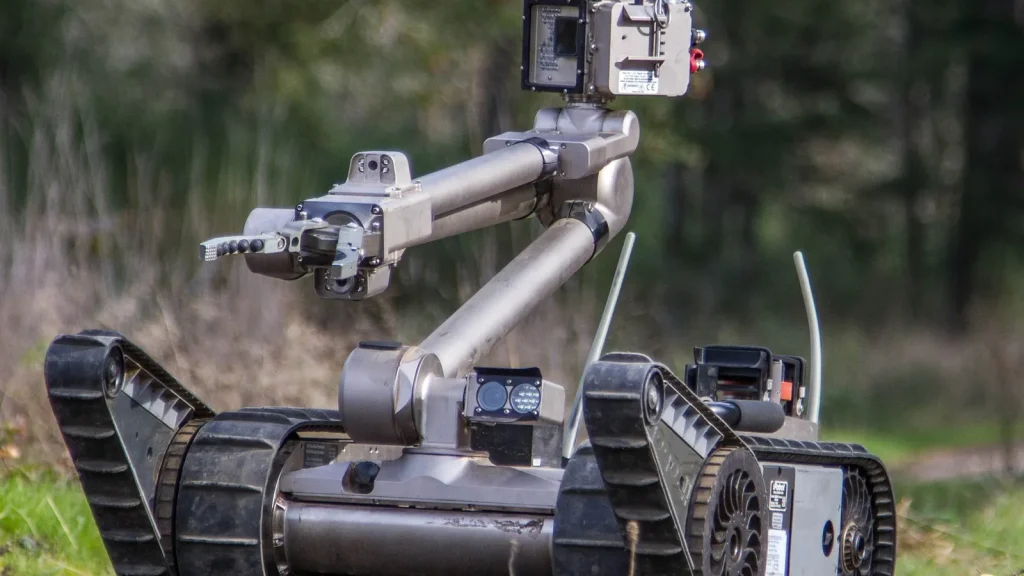

There are three broad categories of humanoid robots in military applications: ground robots, airborne humanoids, and autonomous systems. Each type serves unique functions and offers specific advantages in various combat and support roles.
Transportation robots, for instance, help soldiers transport supplies like artillery and bombs and can even carry human casualties from the battlefield. Firefighting robots assist in extinguishing fires and investigating fire sites during combat situations. Surveillance robots, on the other hand, are employed to gather intelligence on enemy positions and potential threats.
Armed robots equipped with weapons eliminate threats in combat, while mine clearance robots focus on detecting and deactivating land mines, often operated remotely by human controllers. Lastly, search and rescue robots play a vital role in locating missing or captured personnel, particularly in disaster relief scenarios. We will now examine the specifics of these categories.
Ground Robots
Designed for a variety of tasks like transportation, mine clearance, and firefighting, ground robots, or unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs),. These versatile unmanned vehicles are equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, enabling them to operate effectively in hazardous environments.
One prominent example is the PackBot, which features multiple payload bays for functionalities like mine detection and chemical sensing. Another example is the Talon robot, which is equipped with high-powered zoom cameras and gripping arms for the precise and safe disassembly of explosives.
The Odyssey UGV is a notable ground robot in use by the Ukrainian military. This machine:
- It resembles a small, turretless tank
- Can be equipped with a remotely-operated heavy machine gun for combat scenarios
- Can undertake rescue and supply missions
- Can travel up to 30 kilometers on a single charge.
Airborne Humanoids
Representing a cutting-edge innovation in military technology are flying humanoid robots. Recent advancements in lightweight materials and compact propulsion systems have made it possible for these robots to achieve flight, providing new tactical advantages.
These airborne robots are particularly useful in reconnaissance and aerial support roles, where traditional ground robots cannot operate. They can navigate through complex urban environments and provide real-time intelligence to ground forces, significantly enhancing mission effectiveness.
Autonomous Systems
Minimal human input is required for the operation of autonomous humanoid systems. These advanced systems can execute complex tasks with a high degree of autonomy, including the following:
- Navigation
- Surveillance
- Maintenance
- Logistics
The capabilities of these autonomous systems, powered by artificial intelligence, are continually expanding thanks to advancements in AI and robotic technology.
They can perform intricate tasks that were previously impossible without direct human intervention, showcasing the potential of fully autonomous operations in military contexts, including the use of unmanned system technology.
Technological Innovations Driving Humanoid Robotics
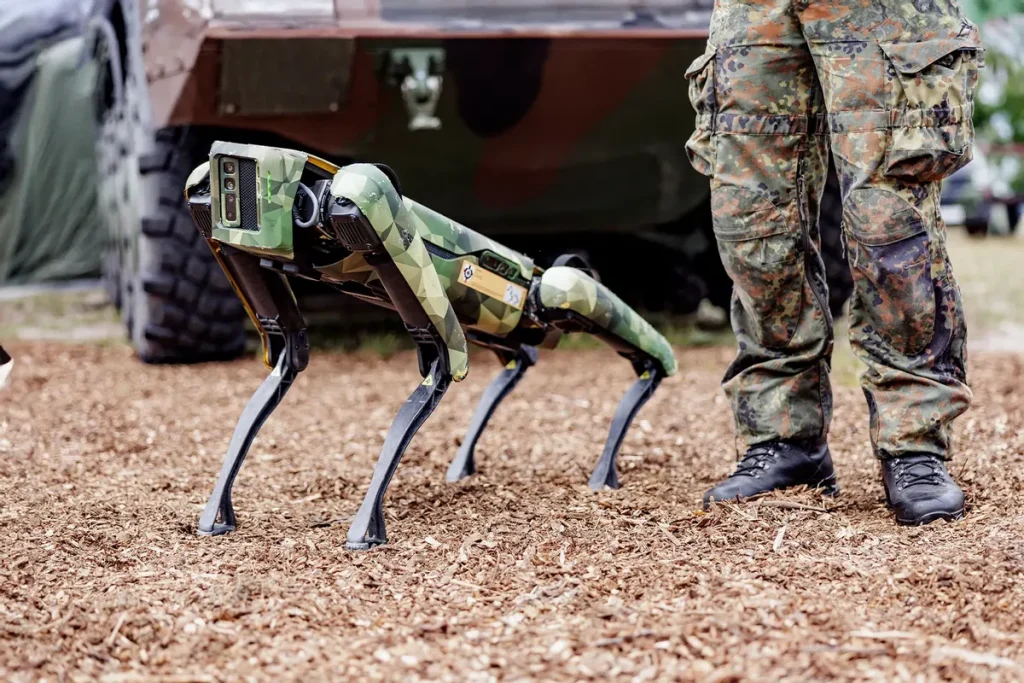

Numerous technological innovations fuel the rapid growth of humanoid robotics in the military. The U.S. Army’s Human-Machine Integration (HMI) initiative aims to integrate advanced AI and robotics with human soldiers to revolutionize battlefield dynamics. This initiative leverages sophisticated AI systems to improve decision-making speed and effectiveness during combat. A human-machine integration demonstration showcases the potential of this groundbreaking technology.
One significant advancement is the integration of augmented reality (AR) interfaces with robotic systems. These AR interfaces enhance situational awareness and decision-making for remote operators, allowing them to control robots more effectively. Additionally, integrating GPS technology with unmanned systems enables robots to automatically know their location, improving navigation and operational efficiency.
Robotic platforms are also becoming more modular, enabling quick adaptation to different missions by swapping out components like sensors and weapon systems. Enhanced autonomy is another focus, allowing robots to carry out missions with minimal human oversight.
Ethical and Legal Implications
The use of military robots raises several ethical and legal issues. One primary ethical issue is the potential for increasing the likelihood of future wars by minimizing human risk. With robots on the front lines, the human cost of war decreases, potentially making it easier for nations to engage in armed conflicts.
Another significant concern is the inability of robots to distinguish between combatants and non-combatants, which could lead to higher civilian casualties. This raises the question of whether robots should have the autonomy to make decisions about killing human beings or if humans should retain this responsibility.
To address these concerns, global study groups, including NATO and allies, are working on developing rules governing the use of robotics in the military. The U.S. Department of Defense has also established AI ethics principles that emphasize:
- Human responsibility
- Avoiding bias
- Ensuring reliability
- Maintaining human oversight.
Case Studies: Humanoid Robots in Action
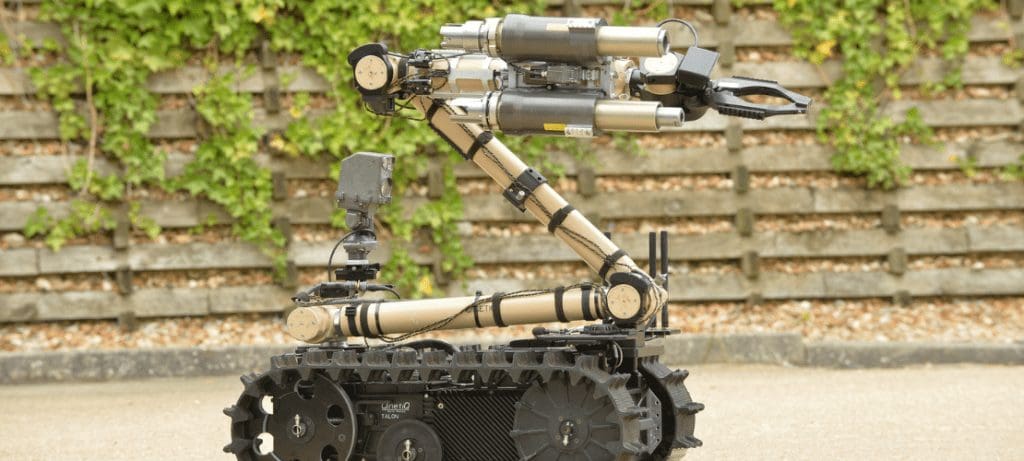
The real-world applications of humanoid robots offer useful insights into their effectiveness and potential. Urban assault exercises, for instance, have demonstrated how robotic vehicles can spearhead attacks by deploying smoke screens, jamming enemy signals, and scouting interiors before human soldiers move in.
This section explores three significant case studies: Project Convergence by the U.S. Army, applications in the Ukrainian military, and deployments in the Middle East. Each case study highlights unique aspects of humanoid robots in action, showcasing their versatility and impact on modern warfare.
Project Convergence
Project Convergence is a U.S. Army initiative aimed at integrating cutting-edge technologies, including humanoid robots, into military operations to enhance combat capabilities. The project focuses on human-machine integration within military formations, aiming to test and refine new tactics and technologies in simulated combat environments.
During Project Convergence, the U.S. Army utilized air and ground robots to support soldiers in complex fights. These robots were equipped with reconfigurable payloads, tethered drones, and counter-drone systems, providing a comprehensive technological support structure.
The project aims to:
- Enhance battlefield effectiveness
- Integrate advanced technology with traditional military strategies
- Demonstrate the potential of humanoid robots in real-world combat scenarios.
Ukrainian Military Applications
The Ukrainian military has been at the forefront of utilizing humanoid robots for various applications. Ukrainian startups have converted abandoned warehouses into facilities for producing military robots, showcasing their innovative spirit in the face of conflict.
These robots are primarily used for reconnaissance missions to gather intelligence behind enemy lines in contested areas and for bomb disposal, significantly reducing the risk to human soldiers on the front lines.
Middle East Deployments
In the Middle East, humanoid robots have been deployed for various combat and support roles, adapting to the unique challenges of the region. These robots have been instrumental in reducing troop exposure to direct combat situations, providing a safer alternative for military personnel.
A specific example includes the use of roving warbots in Iraq, controlled by militias and equipped with cameras for direction and aiming. These robots help minimize the risk to human soldiers while maintaining effective control over combat zones.
Challenges and Obstacles
Several challenges and obstacles remain despite the significant advancements in military robotics. One of the primary issues is leadership changes and budget constraints, which can impede the continuous development and deployment of these advanced systems.
Ethical concerns also pose a significant barrier. The fear of losing humanity in warfare and the moral implications of autonomous decision-making by robots are major points of contention. These concerns often lead to resistance against the widespread adoption of robotic systems in military operations.
Another critical challenge is accountability for mistakes made by autonomous robots. Determining who is responsible when a robot makes an error, particularly if it leads to fatalities, remains a complex legal and ethical issue that needs addressing.
Future Prospects and Army Plans
Army Futures Command is leading efforts to prototype and evaluate new technologies for human-machine integrated formations, promising a bright future for military robotics. This initiative aims to heavily integrate machines into future forces to minimize human risk on the battlefield.
The Army’s Rapid Capabilities and Critical Technologies Office is spearheading the development of these integrated formations, focusing on creating prototypes that combine existing air and ground robotic programs with common architecture and communication systems. This approach ensures a cohesive and efficient deployment of robotic systems.
Financially, the fiscal 2025 budget includes $33 million for initial human-machine integration capabilities for infantry and armor formations. This investment underscores the importance placed on advancing military robotics and integrating them into traditional military strategies.
The Army is also adjusting its acquisition processes to keep pace with rapid technological advancements and emerging threats. Ensuring a functional and user-friendly network, protection from cyberattacks, and appropriate levels of autonomy for systems are key focus areas for army leaders. Army Chief of Staff Gen. Randy George emphasized the importance of adapting to human-machine integration to prevent falling behind adversaries who are willing to use robotics.
Summary
Humanoid robots are undeniably revolutionizing modern warfare, offering significant advantages over traditional combat methods. From reducing human casualties to executing precise operations with minimal errors, these robots have transformed battlefield dynamics.
Technological innovations, such as AI integration and augmented reality interfaces, have propelled the development and effectiveness of these robotic systems. However, ethical and legal concerns continue to challenge their widespread adoption, necessitating careful consideration and regulation.
As we look to the future, the potential of humanoid robots in military operations is immense. With ongoing advancements and strategic investments, these robots are set to play an increasingly critical role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of military personnel. The journey of military robotics is just beginning, promising a future where human-machine integration could redefine warfare as we know it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary types of humanoid robots used in military operations?
The primary types of humanoid robots used in military operations are ground robots, airborne humanoids, and autonomous systems, each serving unique functions such as transportation, reconnaissance, and combat support.
How do humanoid robots reduce human casualties in combat?
Humanoid robots reduce human casualties in combat by taking on dangerous tasks and removing soldiers from direct combat scenarios, ultimately reducing the risk to human lives and allowing safer deployment of military personnel.
What are the ethical concerns associated with the use of military robots?
The ethical concerns surrounding the use of military robots include the potential for increasing the likelihood of wars while minimizing human risk and the inability of robots to distinguish between combatants and non-combatants, leading to higher civilian casualties.
How are technological innovations driving the development of humanoid robots?
Technological innovations like AI integration, augmented reality interfaces, and GPS technology are enhancing the capabilities of humanoid robots, enabling them to perform complex tasks autonomously and improving situational awareness for operators.
What are some real-world examples of humanoid robots in military action?
Real-world examples of humanoid robots in military action include Project Convergence by the U.S. Army, the Ukrainian military’s use of robots for reconnaissance and bomb disposal, and deployments in the Middle East where robots assist in combat and support roles. These instances showcase the increasing integration of robotics in military operations.

One thought on “Humanoid Robots in Military and Defense: Revolutionizing Modern Warfare”